1. Stack Data Structure Using List
 Quy tắc của Stack
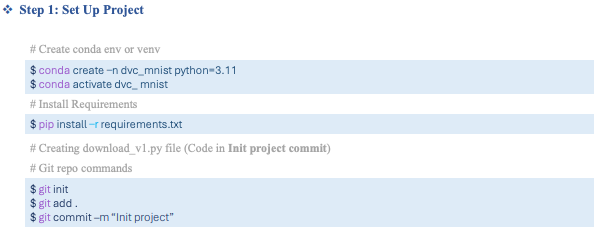
LIFO: Last in first out (Người cuối cùng vào sẽ là người đầu tiên ra)
Phần tử được thêm vào và đi ra chỉ từ một đường duy nhất
Bài tập: Viết Class MyStack
Quy tắc của Stack
LIFO: Last in first out (Người cuối cùng vào sẽ là người đầu tiên ra)
Phần tử được thêm vào và đi ra chỉ từ một đường duy nhất
Bài tập: Viết Class MyStack
-
Code:
class MyStack: def __init__(self, capacity): self.__capacity = capacity self.__stack = [] def push(self, value): self.__stack.append(value) def print(self): vvv
2. Queue
Queue Implementation
Using List: Using deque
from collections import dequeUsing Queue
from queue import QuetueUsing List (OOP) Using dequeue (OOP)
3. Tree Structure
Motivation: Người ta thiết kế ra cấu trúc cây để giải quyết bài toán duyệt phần tử nhanh hơn. Mà bài toán duyệt phần tử được sử dụng rất nhiều → giúp cho các thao tác như tìm kiếm, chèn, xóa trở nên nhanh và hiệu quả hơn.
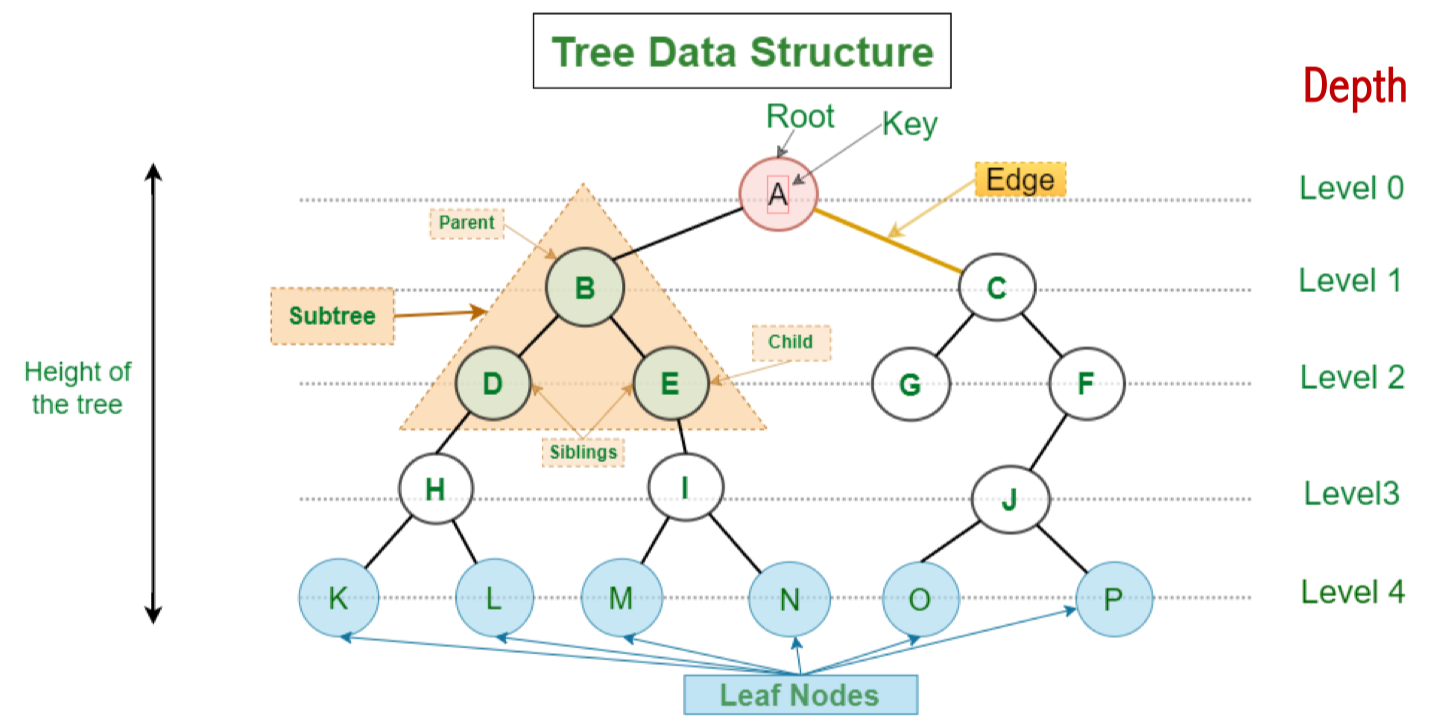
What is a Tree
A non-linear data structure where nodes are organized in a hierarchy
 Các Term:
Các Term:
| Term | Giải thích đơn giản | Ví dụ trong cây |
| Parent Node (Nút cha) | Là nút đứng trên, có nhánh nối đến con | B là cha của D, E |
| Child Node (Nút con) | Là nút được nối ra từ cha | D, E là con của B |
| Root Node (Gốc) | Là nút cao nhất, không có cha | A là gốc cây |
| Leaf Node (Lá) | Là nút không có con nào | K, L, M, N, O, P, G |
| Ancestor (Tổ tiên) | Là tất cả các nút nằm phía trên một nút nào đó | A và B là tổ tiên của E |
| Sibling (Anh em) | Là các nút có cùng cha | D và E là anh em vì đều là con của B |
| Level / Depth (Mức/Độ sâu) | Là số bước đi từ gốc tới nút đó | A: level 0, B: level 1, E: level 2 |
| Subtree (Cây con) | Là 1 phần cây bắt đầu từ 1 nút nào đó + các con cháu của nó | Cây con từ B gồm: B, D, E… |
| Height (Chiều cao) | Là số bước dài nhất từ một nút xuống tới lá | Nếu từ B đến lá xa nhất là 2 bước → height = 2 |
Tree Implementation
Tạo class kiểu dữ liệu TreeNode Lưu ý: Đây không phải cấu trúc Binary Tree nên ta sẽ thiết kế hơi khác.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.children = []
self.parent = NoneCác method trên Tree:
- Thêm node: Tận dụng lại Build-in function của List
class TreeNode:
...
def add_child(self, child):
child.parent = self
self.children.append(child)- Lấy level của node
class TreeNode:
...
def get_level(self): \#to get level of each node
level = 0
p = self.parent
while p:
level += 1
p = p.parent
return level- Vẽ tree:
class TreeNode:
...
def print_tree(self):
space = ' ' * self.get_level() * 3
prefix = space + '|__' if self-parent else ''
print (prefix + self.data) \#add prefix
if self.children:
for child in self.children:
child.print_tree()
- Create tree:
def create_tree():
a_node = TreeNode ("A" )
b_node = TreeNode ("B" )
c_node = TreeNode ("(" )
d_node = TreeNode ("D" )
e_node = TreeNode ("E")
f_node = TreeNode ("F")
g_node = TreeNode("G" )
a_node.add_child(b_node)
a_node.add_child(c_node)
b_node.add_child(d_node)
b_node.add_child(e_node)
c_node.add_child(f_node)
c_node.add_child(g_node)
return a_nodetree = create_tree()
tree.print_tree()
>>A
|__B
|__D
|__E
|__C
|__F
|__GTree Applications
Types of trees
4. Algorithms on Trees
Traversal of Binary Tree
Depth First Search
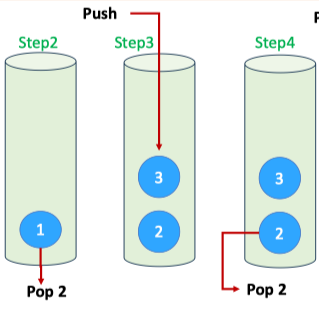
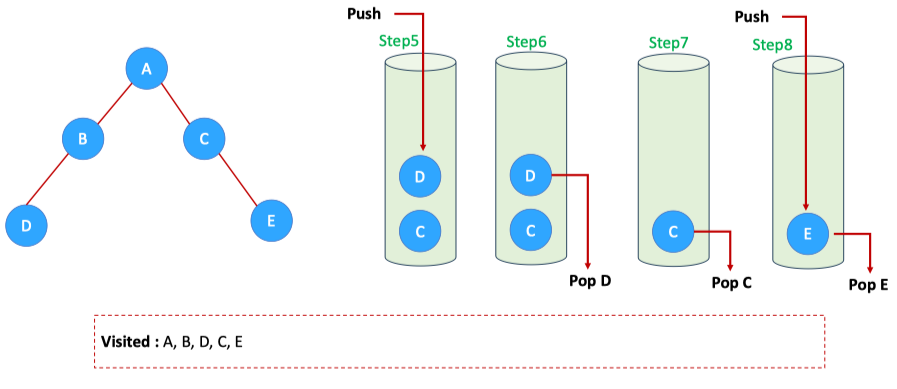 Using Stack
Using Stack
def dfs(sefl):Debug:
Breath First Search
Dùng cấu trúc dữ liệu queue
def bfs(self):
Chạy tay:
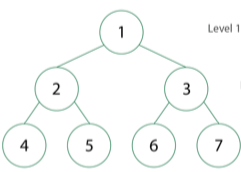
Binary Tree
- Một cây nhị phân là một cấu trúc mà mỗi nút chỉ có nhiều nhất hai nhánh con.
- Mỗi nhánh chia ra như một cái cây thật ngoài đời.
- Mỗi nhánh con có thể tiếp tục chia tiếp — giống như cây có nhiều nhánh con nhỏ.
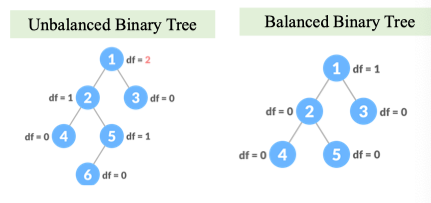
Chiều cao = độ dài của nhánh dài nhất. Độ cao của Tree 1 node = 0
Balanced binary tree
Chiều cao = độ dài của nhánh dài nhất. Độ cao của Tree 1 node = 0 Điều kiện Balance tree:
- Độ dài của các nhánh không lớn hơn 1
- Left subtree is balanced
- Right subtree is balanced
Tại sao phải cân bằng cây?
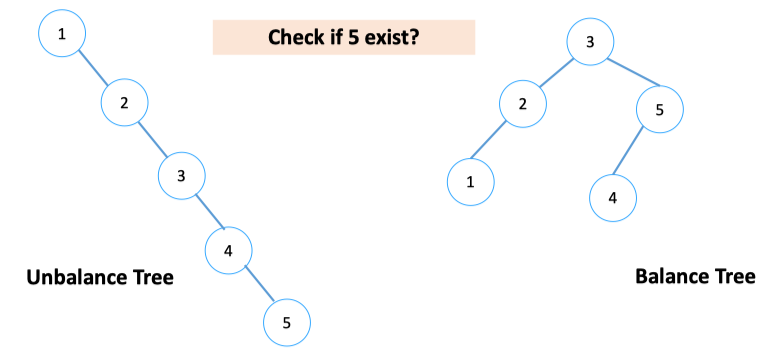 → Khi cây mất cân bằng, việc duyệt cây chả khác gì duyệt trên List ⇒ không tối ưu thời gian và thuật toán tìm kiếm.
→ Khi cây mất cân bằng, việc duyệt cây chả khác gì duyệt trên List ⇒ không tối ưu thời gian và thuật toán tìm kiếm.
Operations On Binary Tree
Insert a Node:
def insert_node(root, key):Cách insert cho cây cân bằng:
→ Sẽ tốn thời gian lúc đầu nhưng về sau cây sẽ cân bằng và tiết kiệm thời gian search. Ý tưởng để đảm bảo cây cân bằng: chèn → kiểm tra cân bằng → ko cân bằng → xoay cho cân bằng. Xoay như nào?
Delete a Node: Trường hợp xóa root:
Tree visualization
Dùng thư viện from graphviz import Graph để vẽ graph:
def draw_tree(root):
Limitations:
Although suitable for storing hierarchical data, binary trees of this general form don’t guarantee a fast lookup. Let’s take as the example the search for number 9 in the above tree.
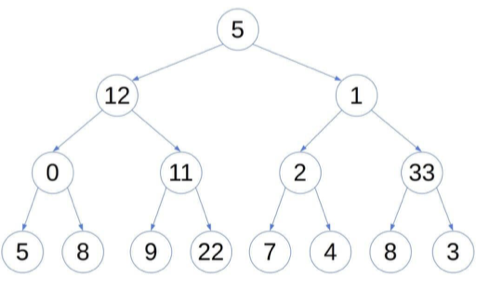 Whichever node we visit, we don’t know if we should traverse the left or the right sub-tree next. That’s because the tree hierarchy doesn’t follow the relation
Whichever node we visit, we don’t know if we should traverse the left or the right sub-tree next. That’s because the tree hierarchy doesn’t follow the relation
Binary Search Tree
- Nhánh trái phải lớn hơn nhánh phải Binary Search Tree Implementation:
class BST:
Search Algorithm in BST: