# skipgram_numpy_from_scratch.py
# Author: you & ChatGPT — Minimal, readable, no deep deps.
import re
import math
import random
import numpy as np
from collections import Counter, defaultdict
# ----------------------------
# 1) Utils
# ----------------------------
def tokenize(text):
"""Tokenize rất đơn giản: chữ thường + tách theo \w+"""
return re.findall(r"[a-zA-Z']+", text.lower())
def build_vocab(tokens, min_count=1):
"""Tạo vocab và lọc từ hiếm."""
freq = Counter(tokens)
vocab = [w for w, c in freq.items() if c >= min_count]
vocab.sort()
word2id = {w:i for i, w in enumerate(vocab)}
id2word = {i:w for w,i in word2id.items()}
counts = np.array([freq[w] for w in vocab], dtype=np.float64)
return word2id, id2word, counts
def subsample_tokens(tokens, counts, word2id, t=1e-5):
"""Subsampling theo paper word2vec: keep prob ~ min(1, sqrt(t/f) + t/f).
Cho corp nhỏ có thể tắt = None."""
if t is None:
return tokens
total = sum(counts)
freqs = {w: counts[word2id[w]] / total for w in word2id}
kept = []
for w in tokens:
if w not in word2id:
continue
f = freqs[w]
p_keep = min(1.0, (math.sqrt(t/f) + t/f))
if random.random() < p_keep:
kept.append(w)
return kept
def make_skipgram_pairs(token_ids, window_size=2):
"""Sinh cặp (center, context) với cửa sổ cố định."""
pairs = []
for i, c in enumerate(token_ids):
left = max(0, i - window_size)
right = min(len(token_ids), i + window_size + 1)
for j in range(left, right):
if j == i:
continue
pairs.append((c, token_ids[j]))
random.shuffle(pairs)
return pairs
def make_unigram_table(counts, power=0.75):
"""Phân phối negative sampling ∝ count^power (không dùng alias table, đủ cho corp nhỏ)."""
p = counts ** power
p = p / p.sum()
return p
def sigmoid(x):
# clip để ổn định số học
x = np.clip(x, -10, 10)
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
def cosine_sim(a, b):
a_norm = a / (np.linalg.norm(a) + 1e-9)
b_norm = b / (np.linalg.norm(b) + 1e-9)
return float(np.dot(a_norm, b_norm))
# ----------------------------
# 2) Skip-Gram NS Model
# ----------------------------
class SkipGramNS:
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim=100, seed=42):
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed)
# Ma trận embedding input (V x D) và output (V x D)
self.W_in = rng.normal(0, 0.01, size=(vocab_size, embed_dim)).astype(np.float64)
self.W_out = rng.normal(0, 0.01, size=(vocab_size, embed_dim)).astype(np.float64)
def train(
self,
pairs,
neg_dist,
neg_k=5,
lr=0.025,
epochs=2,
anneal=True,
report_every=10000
):
"""Huấn luyện SGD từng cặp với K negative."""
V, D = self.W_in.shape
step = 0
for ep in range(1, epochs+1):
random.shuffle(pairs)
total_loss = 0.0
for c_id, o_id in pairs:
# 1) Sample negatives
neg_ids = np.random.choice(V, size=neg_k, replace=True, p=neg_dist)
# Tránh trùng positive context (không bắt buộc)
neg_ids[neg_ids == o_id] = np.random.choice(V, p=neg_dist)
v_c = self.W_in[c_id] # (D,)
u_o = self.W_out[o_id] # (D,)
u_neg = self.W_out[neg_ids] # (K, D)
# 2) Scores
s_pos = np.dot(v_c, u_o) # scalar
s_neg = np.dot(u_neg, v_c) # (K,)
# 3) Sigmoid
p_pos = sigmoid(s_pos) # σ(v·u_o)
p_neg = sigmoid(s_neg) # σ(u_n·v)
# 4) Loss: -log σ(pos) - Σ log σ(-neg)
# log σ(-x) = log(1 - σ(x))
loss = -np.log(p_pos + 1e-12) - np.sum(np.log(1.0 - p_neg + 1e-12))
total_loss += loss
# 5) Gradients
# dL/dv = (σ(pos)-1)*u_o + Σ σ(neg)*u_n
grad_v = (p_pos - 1.0) * u_o + np.sum(p_neg[:, None] * u_neg, axis=0)
# dL/du_o = (σ(pos)-1)*v
grad_uo = (p_pos - 1.0) * v_c
# dL/du_n = σ(neg)*v (cho từng negative)
grad_un = (p_neg[:, None] * v_c[None, :])
# 6) Update
self.W_in[c_id] -= lr * grad_v
self.W_out[o_id] -= lr * grad_uo
self.W_out[neg_ids] -= lr * grad_un
# 7) LR anneal nhẹ theo bước (tùy chọn)
step += 1
if anneal and step % 100000 == 0:
lr = max(lr * 0.9, 0.0005)
if report_every and step % report_every == 0:
avg = total_loss / report_every
print(f"[epoch {ep}] step={step} avg_loss={avg:.4f}")
total_loss = 0.0
def most_similar(self, word, word2id, id2word, topk=10, use='in'):
"""Tìm từ gần nhất theo cosine trong không gian input (mặc định) hoặc output."""
if word not in word2id:
return []
wid = word2id[word]
vec = (self.W_in if use == 'in' else self.W_out)[wid]
mat = self.W_in if use == 'in' else self.W_out
sims = mat @ (vec / (np.linalg.norm(vec) + 1e-9))
# loại chính nó
sims[wid] = -1.0
top_ids = np.argsort(-sims)[:topk]
return [(id2word[i], float(sims[i])) for i in top_ids]
# ----------------------------
# 3) Demo ngắn
# ----------------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
random.seed(0)
np.random.seed(0)
# Một corpus toy; bạn thay bằng văn bản lớn hơn để học tốt hơn
raw_text = """
We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, then, is not an act, but a habit.
The only limit to our realization of tomorrow is our doubts of today.
Not all those who wander are lost. To be, or not to be.
"""
tokens = tokenize(raw_text)
word2id, id2word, counts = build_vocab(tokens, min_count=1)
# (Optional) subsample — với corpus nhỏ, nên tắt để khỏi mất dữ liệu
tokens_kept = subsample_tokens(tokens, counts, word2id, t=None)
token_ids = [word2id[w] for w in tokens_kept if w in word2id]
pairs = make_skipgram_pairs(token_ids, window_size=2)
neg_dist = make_unigram_table(counts, power=0.75)
model = SkipGramNS(vocab_size=len(word2id), embed_dim=50, seed=42)
model.train(
pairs,
neg_dist=neg_dist,
neg_k=5,
lr=0.05,
epochs=5,
anneal=True,
report_every=2000
)
# Thử xem từ gần nhất
query_words = ["not", "be", "habit", "limit", "today"]
for qw in query_words:
sims = model.most_similar(qw, word2id, id2word, topk=5)
print(f"\nNearest to '{qw}':")
for w, s in sims:
print(f" {w:>10s} cos={s:.3f}")
Subsampling
Loại bỏ các tokens có tần suất xuất hiện nhiều nhưng không có quá nhiều ý nghĩa. (Loại bỏ stopword)
def subsample_tokens(tokens, counts, word2id, t=1e-5):
"""Subsampling theo paper word2vec: keep prob ~ min(1, sqrt(t/f) + t/f).
Cho corp nhỏ có thể tắt = None."""
if t is None:
return tokens
total = sum(counts)
freqs = {w: counts[word2id[w]] / total for w in word2id}
kept = []
for w in tokens:
if w not in word2id:
continue
f = freqs[w]
p_keep = min(1.0, (math.sqrt(t/f) + t/f))
if random.random() < p_keep:
kept.append(w)
return keptỞ đây hàm sẽ tính tần suất xuất hiện của từ và so với xác suất giữ lại bằng công thức sau: Trong đó:
- là tần suất của từ
- là tham số ngưỡng được cung cấp (có thể hiểu như một ngưỡng thấp cho tần suất).
- Nếu lớn hơn 1 thì ta lấy 1.
Sau đó Hàm
random.random()sinh ra một số ngẫu nhiên từ 0 đến 1. Nếu giá trị này nhỏ hơn sẽ được giữ lại.
Lựa chọn cặp center
def make_skipgram_pairs(token_ids, window_size=2):
"""Sinh cặp (center, context) với cửa sổ cố định."""
pairs = []
for i, c in enumerate(token_ids):
left = max(0, i - window_size)
right = min(len(token_ids), i + window_size + 1)
for j in range(left, right):
if j == i:
continue
pairs.append((c, token_ids[j]))
random.shuffle(pairs)
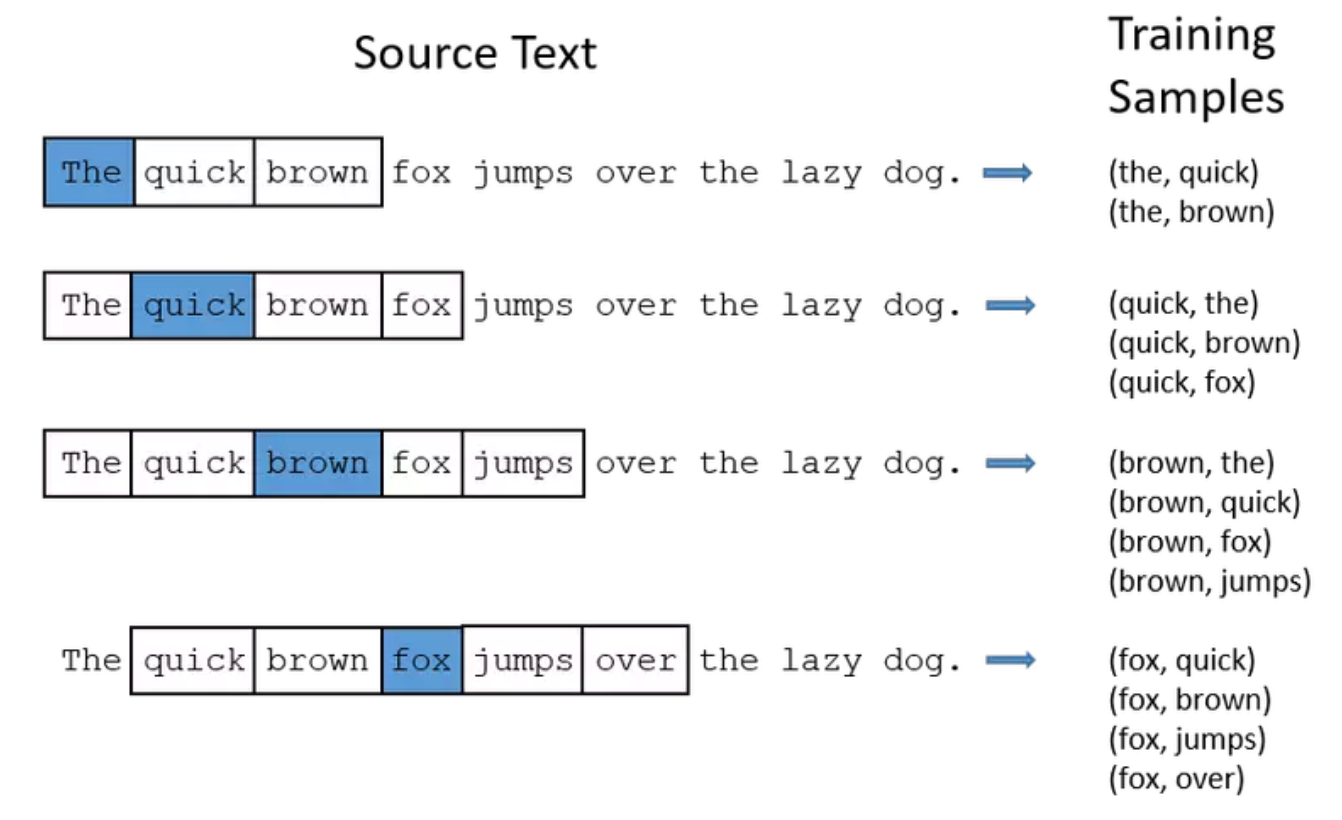
return pairsVí dụ:
Tham số cho class NSkip
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim=100, seed=42):
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed)
# Ma trận embedding input (V x D) và output (V x D)
self.W_in = rng.normal(0, 0.01, size=(vocab_size, embed_dim)).astype(np.float64)
self.W_out = rng.normal(0, 0.01, size=(vocab_size, embed_dim)).astype(np.float64)- Vocab_size: Số lượng từ vựng
- Embed_dim: số lượng chiều Embedding.
Khởi tạo ngẫu nhiên ma trận có kích thước Vocab_size x Embed_dim:
undefinedW_{\text{in}}= \begin{bmatrix} 0.10 & 0.00\ \color{#0b5}{0.00} & \color{#0b5}{0.20}\ -0.10 & 0.10\ 0.05 & -0.05 \end{bmatrix},\qquad W_{\text{out}}= \begin{bmatrix} \color{#0b5}{0.00} & \color{#0b5}{0.10}\ 0.10 & -0.10\ -0.10 & -0.10\ 0.00 & -0.20 \end{bmatrix}
\mathbf v_c = W_{\text{in}}[1] = \begin{bmatrix}0\0.20\end{bmatrix},\quad \mathbf u_o = W_{\text{out}}[0] = \begin{bmatrix}0\0.10\end{bmatrix},\quad \mathbf u_{n_1} = W_{\text{out}}[2] = \begin{bmatrix}-0.10\-0.10\end{bmatrix},\quad \mathbf u_{n_2} = W_{\text{out}}[3] = \begin{bmatrix}0\-0.20\end{bmatrix}.
undefined\begin{aligned} \sigma(s_{\text{pos}}) &\approx \sigma(0.02) \approx \boxed{0.5050},\ \sigma(s_{n_1}) &\approx \sigma(-0.02) \approx \boxed{0.4950},\ \sigma(s_{n_2}) &\approx \sigma(-0.04) \approx \boxed{0.4900}. \end{aligned}
\mathcal{L} = - \log \sigma(\mathbf{v}_c^\top \mathbf{u}o) - \sum{k=1}^{K} \log \sigma(- \mathbf{v}c^\top \mathbf{u}{n_k})
\mathcal L = -\log \sigma(s_{\text{pos}})
- \sum_{k=1}^{2} \log!\bigl(1-\sigma(s_{n_k})\bigr) \approx -\log(0.5050) - \log(0.5050) - \log(0.5100) \approx \boxed{2.039}.